Centipedes, Millipedes, Pauropods, Symphylans (the Myriapods) and Woodlice, Waterlice and Intertidal Isopods (the Isopods) are examples of Arthropods; animals with segmented bodies bearing jointed legs and a hard exoskeleton.
BMIG runs four National Recording Schemes, one each for centipedes, millipedes, woodlice & waterlice and 'marine' intertidal isopods. 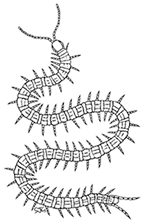
 Centipedes
Centipedes
Centipedes (Class Chilopoda) are recognised by having at least 15 pairs of legs (some immatures have fewer) with a single pair on each trunk segment. They also have large poison claws (forcipules) which are specially modified legs under the head (millipedes do not have these). Their antennae tend to be long and thin (filiform). Centipedes are generally considered to be carnivorous although this may not be true for all groups. More than 50 species, representing four orders of centipede, are found in Britain & Ireland.
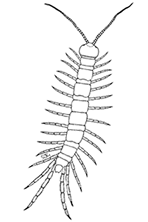
Geophilomorpha (earth centipedes or wire-centipedes), with 25 British species are relatively long, often yellowish or pale (others are reddish-brown) and with 35 – 101 leg pairs (image top right). The three species of Scolopendromorpha have 21 leg pairs and are reddish brown, fast moving types. Lithobiomorpha (stone centipedes) are relatively stout, commonly chestnut or reddish brown and with 15 pairs of relatively long legs (image left). There are 18 species in Britain, all in the genera Lithobius or Lamyctes. Representatives of a fourth order, the Scutigeromorpa (house centipedes) are sometimes found in buildings in mainland Britain and Scutigera coleoptrata occurs outdoors in the Channel Islands. These have very long legs and are usually with very distinct yellow and violet banding on their body and legs as well as compound eyes.
 Millipedes
Millipedes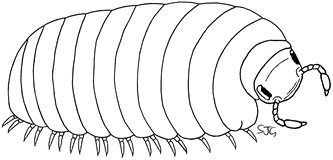
Millipedes belong to the Class Diplopoda and around 65 species from eight orders have been recorded in Britain &Ireland; two only known from hothouse environments. All millipedes can be distinguished from centipedes by the two pairs of legs on most body segments and relatively short clubbed antenae. They also lack the sharp 'poison claws' of the carnivorous centipedes.
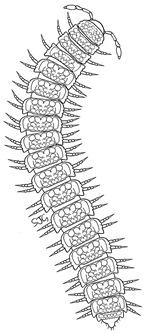
Millipedes have a much greater range of body form than centipedes. The Julida (snake millipedes) represent the typical cylindrical millipedes with 100 or more pairs of legs. Some of the Chourdematida (silk millipedes) are similar in appearence, but have fewer legs. The Polydesmida (flat-back millipedes) are relatively short and broad species (image left) and are often confused with centipedes. The Glomerida (pill millipedes, such as Glomeris - image above right) resemble pill woodlice (Armadillidium sp.). Resembling beetle larvae, the Polyxenida (bristly millipdes) are represented by a single distinctive species Polyxenus lagurus.
Millipedes are generally considered to be detritivores and many species play an essential role in the breakdown of leaf litter. However, some could be considered scavengers feeding on dead animal material; others are herbivores that graze on algae and lichens; a few are considered agricultural or horticultural pests.
Symphylans
Symphylans resemble small, white centipedes with one pair of legs per body segment but they have only 12 pairs of legs (often only 11 pairs visible) and lack poison claws. They also lack eyes and the rear end bears a pair of prominent conical cerci bearing setae. The British checklist currently includes just 14 species but the group have not been well studied. Mainly due to their small size they can be difficult to identify.
They can often be seen running rapidly over the soil surface when stones are turned over. They occur in all sorts of soils and can be present in large numbers. Some species can sometimes become a serious greenhouse or outdoor pest attacking the roots of young plants.
Pauropods
Pauropods are the smallest of the myriapods, just 1-2mm long with 9-11 leg bearing segments in the adult. They can be recognised by their branched antennae. All but one of the 23 species recorded from Britain have an elongate body form. Due to their small size they can be difficult to identify.
Few BMIG members have seen these animals in the field although very large densities have been reported from soil samples in some studies. They are widely distributed in leaf litter and soil and can also be found under stones and dead wood. They can easily be mistaken for small slow moving collembola, but pauropods are able to run rapidly forwards when disturbed, suddenly stop, then run backwards or twist their bodies in many directions.
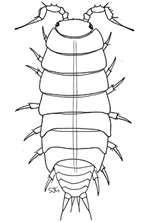 Woodlice and Waterlice
Woodlice and Waterlice
Woodlice and Waterlice belong to the Crustacean Order Isopoda, which means ‘equal feet’. This is a reference to their seven pairs of more or less identical legs. The body comprises 12 segments and is flattened from top to bottom to facilitate walking. Most Isopods are marine and the fossil record suggests that woodlice evolved from their marine ancestors relatively recently, to colonise dry land, around 50 mya.
Britain’s non-marine Isopods are divided into two sub-orders: Asellota, the Aquatic Waterlice, and Oniscidea, the Terrestrial Woodlice. Just four species of waterlouse and about 40 species of woodlouse are known to occur in the wild in Britain (Gregory, 2009). About 15 additional woodlice are known from inside heated glasshouses (such as botanical gardens and butterfly houses). Woodlice and waterlice are detritivores, mainly feeding upon organic detritus, such as dead leaves, dead wood, etc. Some will also graze algae and fungi.
Intertidal Isopods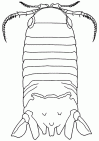
Woodlice and waterlice are not the only isopods found in Britain. Many others live in the seas and coasts areas around Britain, with about 70 species of isopod found in the intertidal zone. Most marine isopods share the characteristics of woodlice and waterlice, but they come in a dazzling array of shapes and sizes, some tiny and woodlice-like, others large or elongated, still others internal parasites with radically transformed bodies so that they are barely 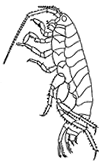 recognisable as members of the same order. Most are detritivores or feed on algae, whilst others bore in wood, are voracious scavengers, or parasitise fish and other crustaceans. They belong to a wide range of sub-orders, super-families and families within the order Isopoda.
recognisable as members of the same order. Most are detritivores or feed on algae, whilst others bore in wood, are voracious scavengers, or parasitise fish and other crustaceans. They belong to a wide range of sub-orders, super-families and families within the order Isopoda.
Landhopper - Arcitalitrus dorrieni
The Landhopper, also known as Woodhopper or Lawn Shrimp, is the only truly terrestrial anmphipod occuring in the British Isles. It is not native, but originates from Eastern Australia, and was first found in Britain early in the 20th Century.
Arcitalitrus dorrieni has been adopted by BMIG as an "honorary woodlouse" to provide a focus for recording.
